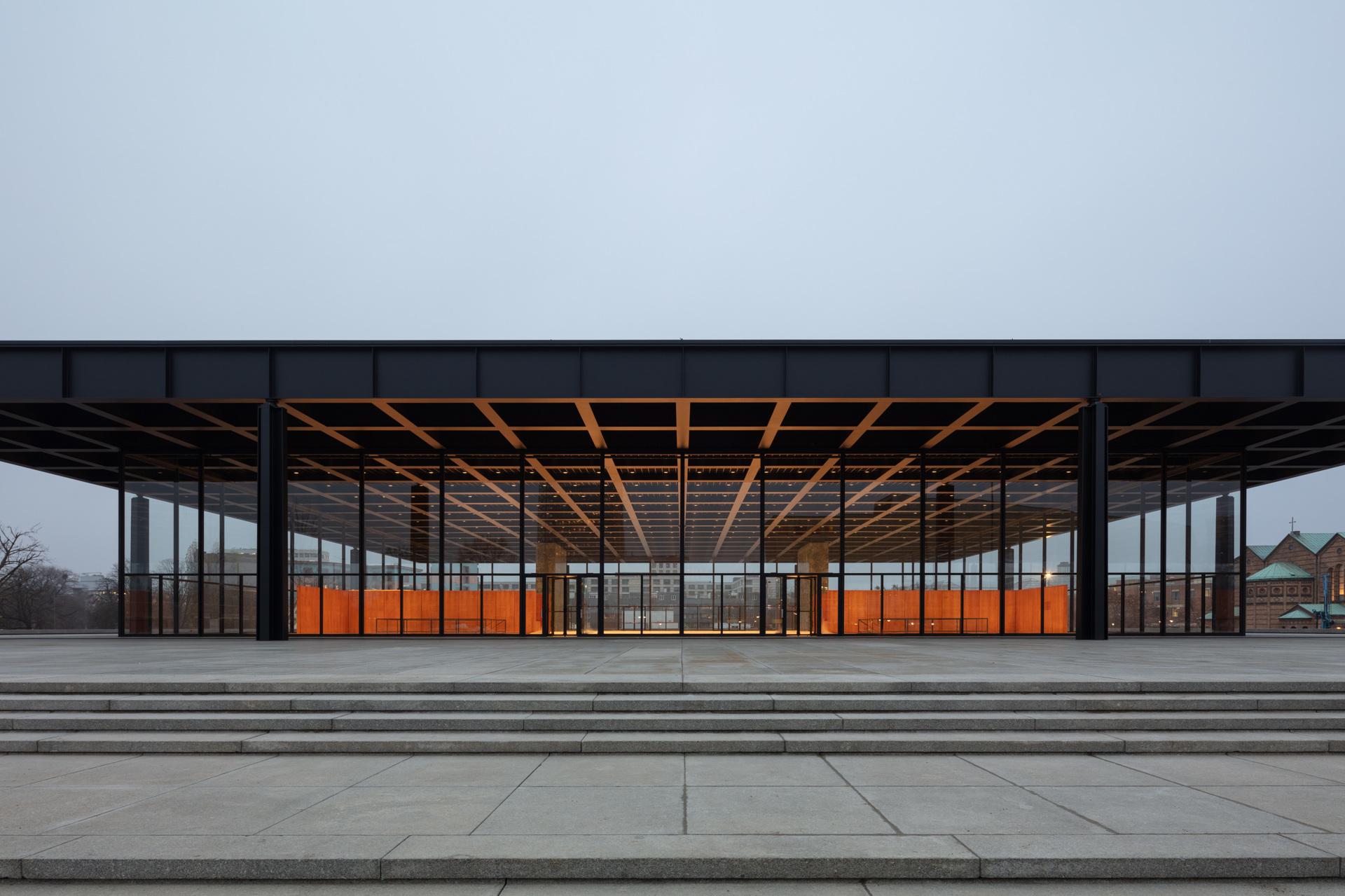
Neue Nationalgalerie | Berlin
The New National Gallery Berlin, built in 1965-68, is one of the landmarks of modern architecture and was included in the list of monuments of the State of Berlin. For the recent refurbishment of the New National Gallery (NNG) from 2015 - 2021, SLT was allowed to contribute by supplying new or modified revision of existing and listed ventilation components. Primarily, however, we were able to use our know-how and with the help of our in-house laboratory to develop a facade covering suitable for a museum, which does justice to the climatic requirements of the listed building by the architect Ludwig Mies van der Rohe. It was necessary to use an effective segment jet nozzle system to counteract the drop in cold air on the 8 m high glass façade typical of the NNG and to reduce possible condensation on the single-pane glazing on cold winter days. In this way, exhibited art is protected from temperature and humidity fluctuations, which can otherwise cause serious damage to exhibits.
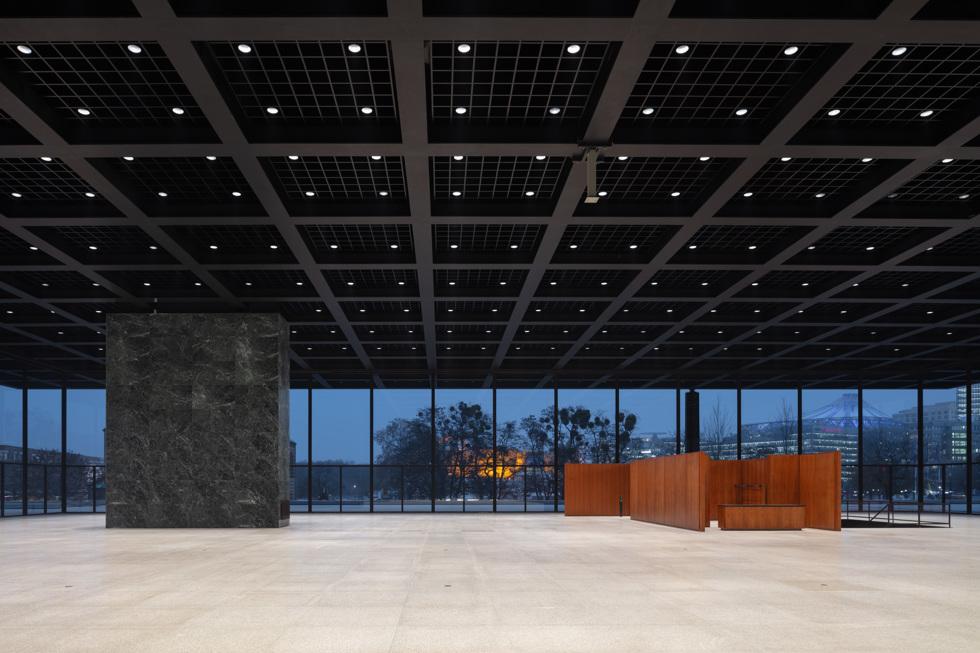

On behalf of the company Domann Beratende Ingenieure GmbH, we developed a segment jet nozzle system for the glass facade of the New National Gallery in Berlin, which is a listed building. In order to prevent cold air from falling through the single pane glazing installed on site in extreme outside temperatures, the 8 m high glass facade is to be covered with warm supply air. A central question during the curtaining was whether the crossbar installed at a height of 2.7 m was surrounded by the rising supply air and whether the air flow was not torn off from the facade.
LABORATORY TESTS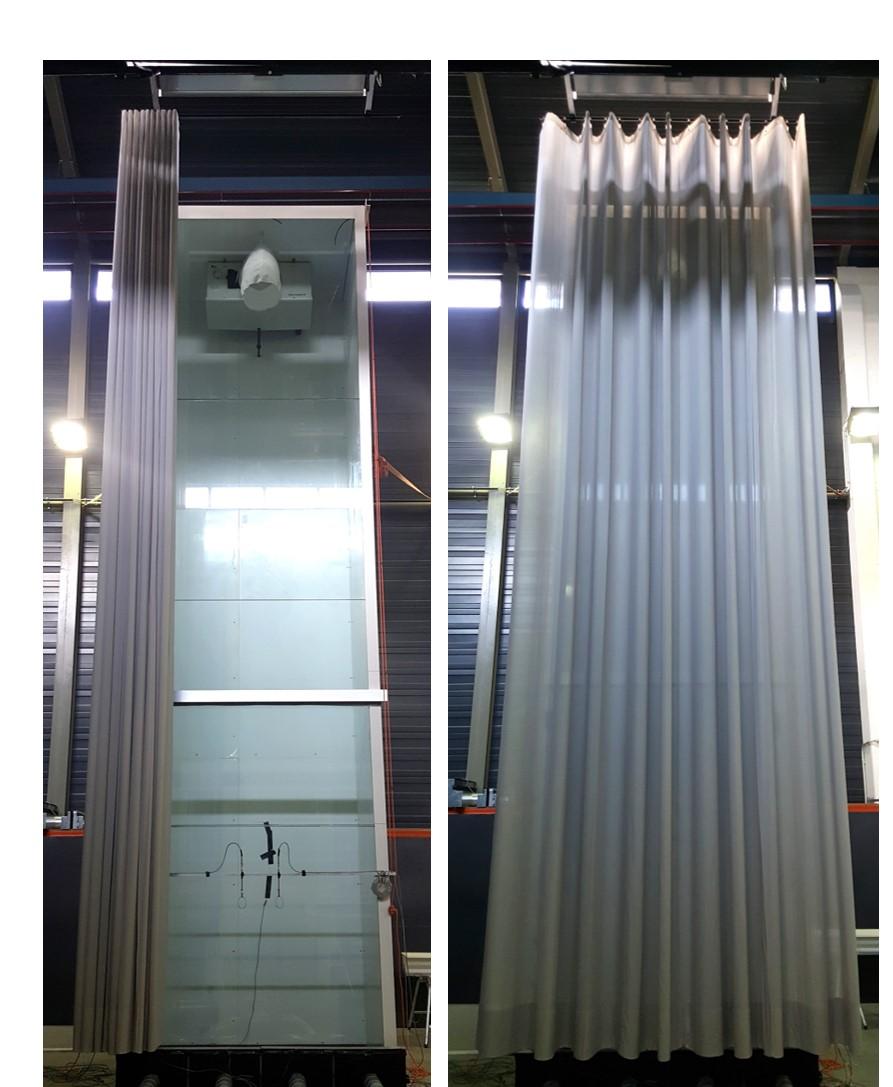
The segment jet nozzle system used was examined in a laboratory test using the original facade lattice structures (Fig. 1a) in order to evaluate the generated fogging of the glass facade and to confirm the functionality and effectiveness of the shielding. For this purpose, a walk-in deep-freeze cell was created for the laboratory test and set up in the in-house SLT laboratory. The deep-freeze cell with the dimensions 2100 x 8000 x 1500 mm consists of a housing with insulation made of 100 mm polyurethane hard foam in a segmented design.
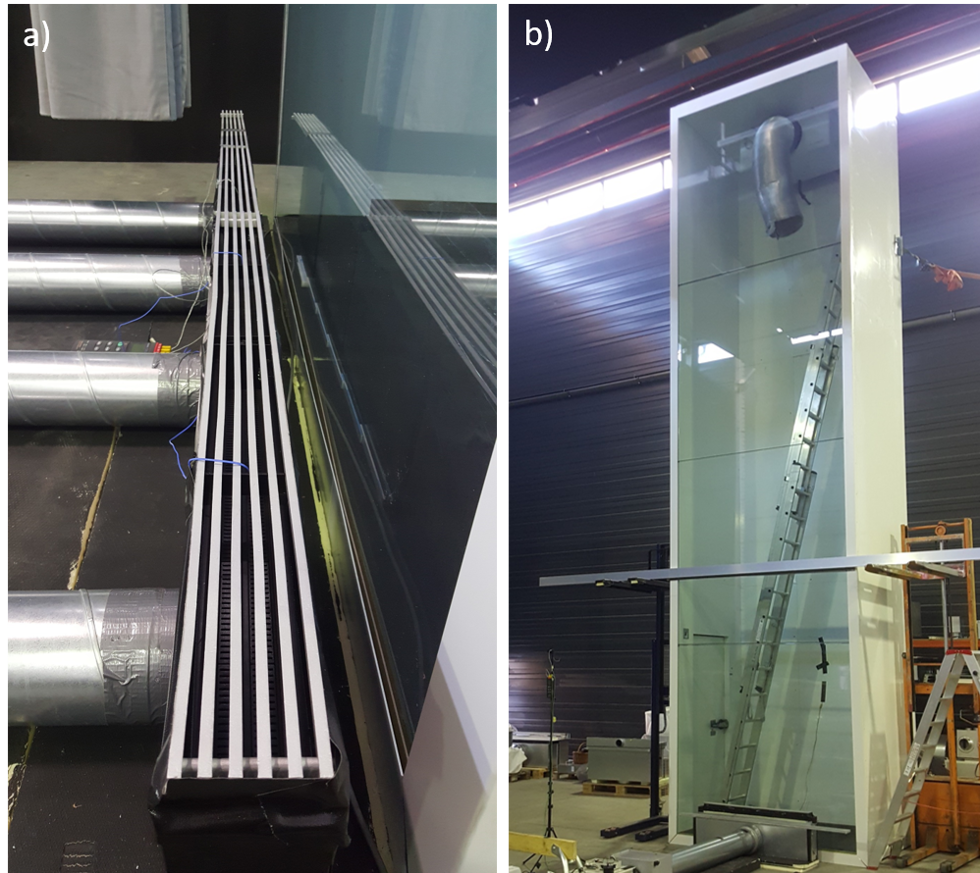
Fig. 1 shows the test components in the ventilation laboratory for investigations into the air conditioning of the NNG facade. a) The segment jet nozzle system with the original facade lattice structures and b) the cold room with single pane glazing in the construction stage, the transom is at a height of 2.7 m.
Similar to the original NNG room, the front of this cell consists of single pane glazing and is conditioned accordingly by the cold cell. As in the original, the IBD system was installed in the floor area - outside the cold room - and the intended air volume was applied in order to provide evidence that the cold air drop is prevented. The room temperature (laboratory) can be raised up to 28°C, so that there are sufficient variation options when setting the process-influencing parameters - outside and inside - which are then also measured and documented. In order to be able to reproduce the real situation on site, a transom/transom was installed at a height of 2.7 m. To solve the task, the necessary air speeds and temperatures were measured with the appropriate technology. In addition, the tests were recorded using video documentation and the results obtained were compared with the results of a CFD simulation.

Fig. 2: Part of the measuring equipment used is used to record the air temperatures and air speeds in front of the facade and is placed up to a height of 8 m.
RESULTS OF THE INVESTIGATIONS
The IBD segment jet nozzle system used creates an effective haze on the glass facade. Based on the tests carried out and the simulation, it was possible to show that the façade is exposed to the incoming supply air up to a height of 8 m. The installed transom is also successfully flown around, so that the upper half of the facade is also heated up. The inflow and heating of the facade counteracts a drop in cold air and prevents or reduces the formation of condensation on the glass surface.
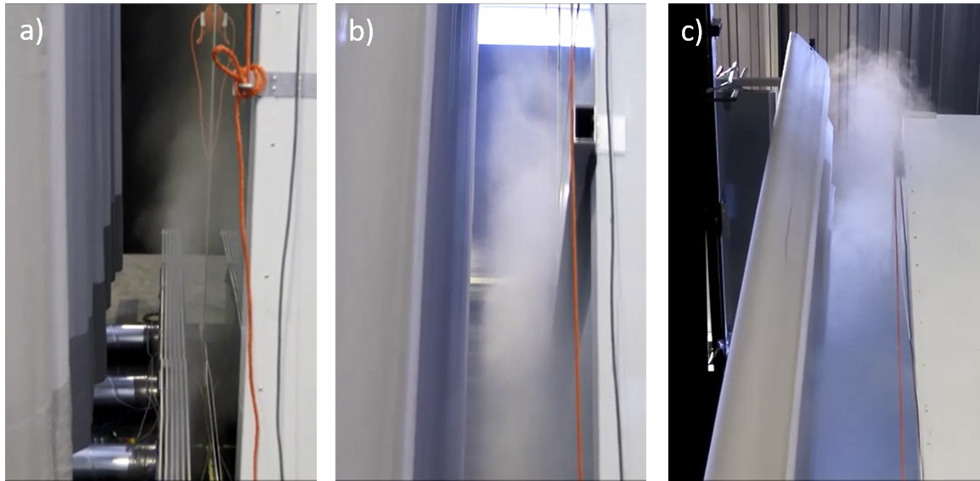
Fig. 3: Fog test: The incoming air is mixed with a vaporized fog fluid in order to visualize the flow characteristics. a) The air escapes from the facade grille and settles on the glass facade, b) the supply air flows around the cross bar and is not torn off the facade, c) the fresh air flows along the 8 m high facade beyond the cold storage cell.
CONCLUSION
Using existing, listed components, a facade curtain for conditioned supply air was developed, which corresponds to the current state of the art and was integrated into the existing architecture in the course of the measures. The refurbishment, using special, laboratory-tested air flow elements, resulted in a significant improvement, so that the listed single-pane glazing can be air-conditioned to an acceptable level in both summer and winter, and the loss of condensate can be reduced to a minimum.
You can find out more about the air conditioning of the NNG using the IBD segment jet nozzle system here:
https://blog.smb.museum/gemaessigte-zone-die-klimatechnik-in-der-neuen-nationalgalerie/
Deployed Products
The NRA is a manually adjustable diffuser that can create horizontal radial jets as well as vertical jets. The system consists of a round diffuser body with a spigot for direct installation in an air duct system as well as the interior air guiding and adjusting unit. This air guiding and adjusting unit is a combination of a circular guiding element and a baffle plate arranged in a defined vertical distance. This unit can be moved vertically and locked into place within the diffuser body, making every jet geometry from horizontal or bell-shaped to vertical configurable. The diffuser is especially well suited for usage in shopping malls, sport halls, market halls, multipurpose halls and production halls because high air volumes can be moved easily. Installation can be done flush with ceiling or freely suspended.
KRLThe KRL is a radial flow diffuser with a perforated front panel. The air flow occurs through rigid diffuser-like air guiding elements to create radial horizontal jets. The front-sided perforation ensures an even air flow. The special construction guarantees a high air flow at low sound power levels. The front panel is mounted by a central screw (size 800 with additional screws at the edges).
IBDThe IBD is a special diffuser designed for having high vertical or horizontal throw distances, depending on application. The diffuser is equipped with high-speed nozzles that achieve high induction and high throw distances at low sound levels. Due to the compact construction and the high, specific flow rates, the diffuser is primarily suited for use in special projects.
RQLThe ventilation grille RQL consists of rigid, square aluminium bars with a surrounding frame. The mounting is done by screws through the frame.
